|
|
Saudi
Arabia Introduction
Saudi
Arabia is a monarchy in southwestern Asia, and
occupies most of the Arabian Peninsula. Saudi Arabia
is bordered on the north by Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait;
on the east by the Persian
Gulf and Qatar; on the southeast by the United
Arab Emirates and Oman on the south by the Republic
of Yemen; and on the west by the Red Sea and the
Gulf of Aqaba. The southeast and southern
boundaries are not precisely defined.
|
Saudi
Arabia Fun
Fact
If
you are not a Muslim, you may not enter Saudi Arabia
without an invitation and you may not leave without
an exit permit. Visitors to Saudi Arabia are subject
to the same rigorous Islamic law as Saudis. It
is not uncommon for Westerners to be imprisoned
for possessing illegal substances such as alcohol,
pornography, pork or narcotics. Thieves still have
their hands amputated and capital crimes are punished
by public beheadings.
|
Geert
Hofstede Analysis for
Saudi Arabia
|
|
|
The Geert Hofstede analysis for Saudi Arabia is almost identical
to other Arab countries their Muslim faith plays a large
role in the people’s lives. Large power distance and
uncertainty avoidance are the predominant characteristics
for this region. This indicates that it is expected and accepted
that leaders separate themselves from the group and issue
complete and specific directives.
The
Geert Hofstede analysis for the Arab World, that
includes the countries of Egypt, Iraq, Kuwait,
Lebanon, Libya, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab
Emirates, demonstrates the Muslim faith plays a
significant role in the people’s lives.
Large
Power Distance (PDI) (80) and Uncertainty Avoidance
(UAI) (68) are predominant Hofstede Dimension characteristics
for the countries in this region. These societies
are more likely to follow a caste system that does
not allow significant upward mobility of its citizens.
They are also highly rule-oriented with laws, rules,
regulations, and controls in order to reduce the
amount of uncertainty, while inequalities of power
and wealth have been allowed to grow within the
society.
When
these two Dimensions are combined, it creates a
situation where leaders have virtually ultimate
power and authority, and the rules, laws and regulations
developed by those in power reinforce their own
leadership and control. It is not unusual for new
leadership to arise from armed insurrection – the
ultimate power, rather than from diplomatic or
democratic change.
The
high Power Distance (PDI) ranking is indicative
of a high level of inequality of power and wealth
within the society. These populations have an expectation
and acceptance that leaders will separate themselves
from the group and this condition is not necessarily
subverted upon the population, but rather accepted
by the society as their cultural heritage.
The
high Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI) ranking
of 68, indicates the society’s low level
of tolerance for uncertainty. In an effort to minimize
or reduce this level of uncertainty, strict rules,
laws, policies, and regulations are adopted and
implemented. The ultimate goal of these populations
is to control everything in order to eliminate
or avoid the unexpected. As a result of this high
Uncertainty Avoidance characteristic, the society
does not readily accept change and is very risk
adverse.
The
Masculinity index (MAS), the third highest Hofstede
Dimension is 52, only slightly higher than the
50.2 average for all the countries included in
the Hofstede MAS Dimension. This would indicate
that while women in the Arab World are limited
in their rights, it may be due more to Muslim religion
rather than a cultural paradigm.
The
lowest Hofstede Dimension for the Arab World is
the Individualism (IDV) ranking at 38, compared
to a world average ranking of 64. This translates
into a Collectivist society as compared to Individualist
culture and is manifested in a close long-term
commitment to the member 'group', that being a
family, extended family, or extended relationships.
Loyalty in a collectivist culture is paramount,
and over-rides most other societal rules.
More Geert Hofstede Details
Written
by Stephen Taylor - the Sigma
Two Group
|
|
Religion
in Saudi Arabia
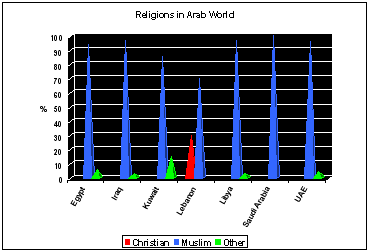
*
WORLD FACTBOOK 2002
The
predominant religion for Egypt is Islam, the practice
of the Muslim faith. (see Article)
An
Imam explains Islam
By IMAM SHAMSHAD A. NASIR
Islam
is the name of the religion that was founded 1,400
years ago by the Holy Prophet of Islam, Muhammad.
Islam is an Arabic word which means peace, love
and complete submission and obedience to God. There
is no difference between Islam and Muslims. Islam
is the religion that a Muslim follows, just as
Christianity is the religion which a Christian
follows.
A
Muslim is someone who has accepted Islam and lives
his whole life according to the teachings of Islam.
A true Muslim is one who is loving and caring,
promotes peace, and is fully obedient and submissive
to the will of God.
Islam
demands from its believers that they establish
peace in the world, promote love and make such
examples of themselves that others, knowing that
they are Muslims, feel at peace and harmony in
that knowledge. This is the true Islam and what
it means to be a Muslim.
The
Holy Prophet of Islam has said that a true Muslim
is one whose actions and words do not harm his
fellow man.
ISLAMIC
GREETINGS
When Muslims greet each other, instead
of saying, “good morning” or “hello” they
say “Assalamo Alaikum,” which means “May
peace be upon you and may God's blessings be with
you.” This greeting makes a Muslim aware that
he has to spread love and peace wherever he goes.
ATTRIBUTES
OF GOD
There are many attributes of God, one being “AsSalam” meaning “the
Bestower of peace and love.” Man has been created
to fashion himself to the attributes of God and Muslims
must try to adopt this attribute of God.
If
someone calling himself a Muslim and a follower
of the Holy Prophet does not promote peace and
love in his actions and does not follow this teaching,
he cannot be a true follower of the Holy Prophet.
A
MUSLIM'S PRAYERS
Muslims pray five times a day, asking God
for his love.
They
pray, “Oh God! You are Peace and from you,
is Peace; Blessed are you, O Lord of Majesty and
Bounty.”
THE
RELIGION OF ISLAM
Islam is a religion from God for the whole
of mankind and the name Islam was given to the Muslims
by God himself in the Holy Quran.
“This
day have I perfected your religion for you and
completed my favour upon you and have chosen for
you Islam as religion.”
The
Holy Quran has been sent for the guidance of mankind.
It is full of wisdom and commands.
|
Saudi
Arabia Appearance
 Never
show bare shoulders, stomach, calves and thighs. Never
show bare shoulders, stomach, calves and thighs.
 Visitors
are expected to abide by local standards of modesty
however, do not adopt native clothing. Traditional
clothes on foreigners may be offensive. Visitors
are expected to abide by local standards of modesty
however, do not adopt native clothing. Traditional
clothes on foreigners may be offensive.
 Despite
the heat, most of the body must always remain covered. Despite
the heat, most of the body must always remain covered.
 A
jacket and tie are usually required for men at
business meetings. Men should wear long pants and
a shirt, preferably long-sleeved, buttoned up to
the collar. Men should also avoid wearing visible
jewelry, particularly around the neck. A
jacket and tie are usually required for men at
business meetings. Men should wear long pants and
a shirt, preferably long-sleeved, buttoned up to
the collar. Men should also avoid wearing visible
jewelry, particularly around the neck.
 Women
should always wear modest clothing in public. High
necklines sleeves at least to the elbows are expected.
Hemlines, if not ankle-length should at least be
well below the knee. A look of baggy concealment
should be the goal, pants or pant suits are not
recommended. It is a good idea to keep a scarf
handy, especially if entering a Mosque. Women
should always wear modest clothing in public. High
necklines sleeves at least to the elbows are expected.
Hemlines, if not ankle-length should at least be
well below the knee. A look of baggy concealment
should be the goal, pants or pant suits are not
recommended. It is a good idea to keep a scarf
handy, especially if entering a Mosque.
|
| |
Saudi
Arabia Behavior
 It
is common to remove your shoes before entering
a building. Follow the lead of your host. It
is common to remove your shoes before entering
a building. Follow the lead of your host.
 Alcohol
and pork are illegal. Alcohol
and pork are illegal.
 In
the Muslim world, Friday is the day of rest. In
the Muslim world, Friday is the day of rest.
 There
are several styles of greetings used; it is best
to wait for your counterpart to initiate the greeting.
Men shake hands with other men. Some men will shake
hands with a woman; it is advisable for a businesswoman
to wait for a man to offer his hand. A more traditional
greeting between men involves grasping each other’s
right hand, placing the left hand on the other’s
right shoulder and exchanging kisses on each cheek. There
are several styles of greetings used; it is best
to wait for your counterpart to initiate the greeting.
Men shake hands with other men. Some men will shake
hands with a woman; it is advisable for a businesswoman
to wait for a man to offer his hand. A more traditional
greeting between men involves grasping each other’s
right hand, placing the left hand on the other’s
right shoulder and exchanging kisses on each cheek.
 The
left hand is considered unclean and reserved for
hygiene avoid gestures with the right hand. Do
not point at another person and do not eat with
the left hand. The
left hand is considered unclean and reserved for
hygiene avoid gestures with the right hand. Do
not point at another person and do not eat with
the left hand.
 Men
walking hand in hand is a sign a friendship. Men
walking hand in hand is a sign a friendship.
 Try
not to cross your legs when sitting. Never show
the bottom of your feet. Try
not to cross your legs when sitting. Never show
the bottom of your feet.
 The "thumbs
up" gesture is offensive. The "thumbs
up" gesture is offensive.
 Gifts
are not necessary, but appreciated. Avoid admiring
an item too much, you host may feel obligated to
give it to you. When offered a gift, it is impolite
to refuse. Gifts
are not necessary, but appreciated. Avoid admiring
an item too much, you host may feel obligated to
give it to you. When offered a gift, it is impolite
to refuse.
 Women
in Saudi Arabia are not permitted to drive vehicles. Women
in Saudi Arabia are not permitted to drive vehicles.
|
| |
Saudi
Arabia Communications
 Do not discuss the subject
of women, not even to inquire about the health
of a wife or daughter. The topic of Israel should
also be avoided. Sports is an appropriate topic. Do not discuss the subject
of women, not even to inquire about the health
of a wife or daughter. The topic of Israel should
also be avoided. Sports is an appropriate topic.
 Names are often confusing.
It’s best to get the names (in English) of
those you will meet, speak to, or correspond with
before hand. Find out both their full names and
how they are to be addressed in person. Names are often confusing.
It’s best to get the names (in English) of
those you will meet, speak to, or correspond with
before hand. Find out both their full names and
how they are to be addressed in person.
 Communications occur at
a slow pace. Do not feel obligated to speak during
periods of silence. "Yes" usually means "possibly". Communications occur at
a slow pace. Do not feel obligated to speak during
periods of silence. "Yes" usually means "possibly".
 Your Saudi host may interrupt
your meeting or conversation, leave the room and
be gone for 15 to 20 minutes for the purpose of
his daily prayers. Your Saudi host may interrupt
your meeting or conversation, leave the room and
be gone for 15 to 20 minutes for the purpose of
his daily prayers.
 At a meeting, the person
who asks the most questions is likely to be the
least important. The decision maker is likely a
silent observer. At a meeting, the person
who asks the most questions is likely to be the
least important. The decision maker is likely a
silent observer.
 A customary greeting is salaam
alaykum. Shaking hands and saying kaif
hal ak comes next. A customary greeting is salaam
alaykum. Shaking hands and saying kaif
hal ak comes next.
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
HOME
PAGES
|
|
|
|
|
Resources
Geert Hofstede Free
Monthly Newsletter Resource
Page
International
Business Center
|
|
|
|
|
|

Thanks
to the UTD Global MBA graduates who work
diligently on collecting the information for this Website. |
Page authored by: Patty Butler
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|